In the wake of Hurricane Harvey and the devastating flooding it caused, many people have been talking about water management. Texas has always been prone to natural disasters, but with climate change making these events more frequent, it is more important than ever to have a good water management plan in place. In this blog post, we will discuss the importance of good water management and how it can help your community prepare for future natural disasters.
What Natural Disasters Have Impacted Texas?
Texas has been hit by a number of natural disasters in recent years, including Hurricane Harvey, Hurricane Ike, the drought of 2011-2015, and the Bastrop wildfires. Each of these events has had a significant impact on Texas communities and highlighted the importance of good water management.
Hurricane Harvey was particularly devastating, causing $125 billion in damage and claiming more than 100 lives. The hurricane made landfall in Texas on August 17, 2017, and brought with it unprecedented levels of rainfall. Houston was hit particularly hard, with some areas receiving more than 50 inches of rain in just a few days.
The flooding caused by Hurricane Harvey was the worst in US history, and it took months for the affected communities to recover. The water damage alone affected hundreds of thousands of homes and displeased more than 30,000 people. In the aftermath of the hurricane, it became clear that many Texas communities lacked a good water management plan and were not prepared for such a large-scale event.
What Is Water Management?
Water management is the process of managing water resources in a way that meets the needs of people and ecosystems. It involves planning for and responding to both short-term and long-term water needs, including floods, droughts, and other natural disasters.
Good water management is essential for keeping communities safe during times of crisis. It can help reduce the risks associated with all-natural disasters and damage to infrastructure.
How Can Water Management Help Communities Prepare for Natural Disasters?
Water management can help communities prepare for natural disasters in a number of ways.
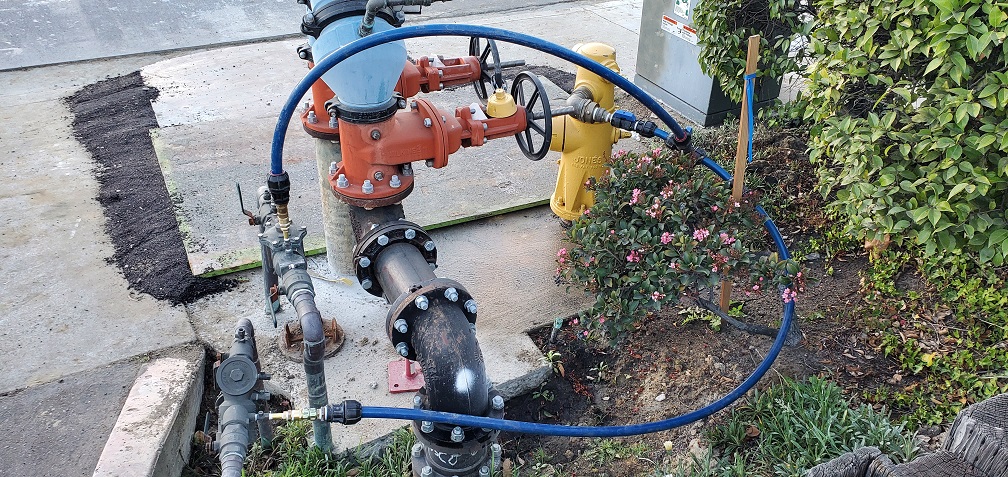
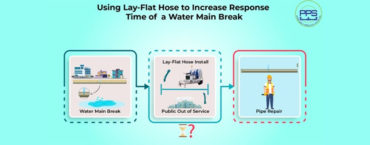
-Flooding: A good water management plan can help reduce the risk of flooding by optimizing the transportation of floodwater out of affected areas. The best tool for this challenge is an emergency response trailer equipped with a high-quality lay flat hose. It can also help improve drainage systems and keep stormwater from overflowing into streets and homes.
-Drought: Optimized resources can help communities prepare for drought by regulating water use and conserving resources. It can also help to identify areas that are most at risk for drought and develop strategies to address them. We will see a greater need for drought solutions in the coming years as Texas continues to use up its underground water stores.
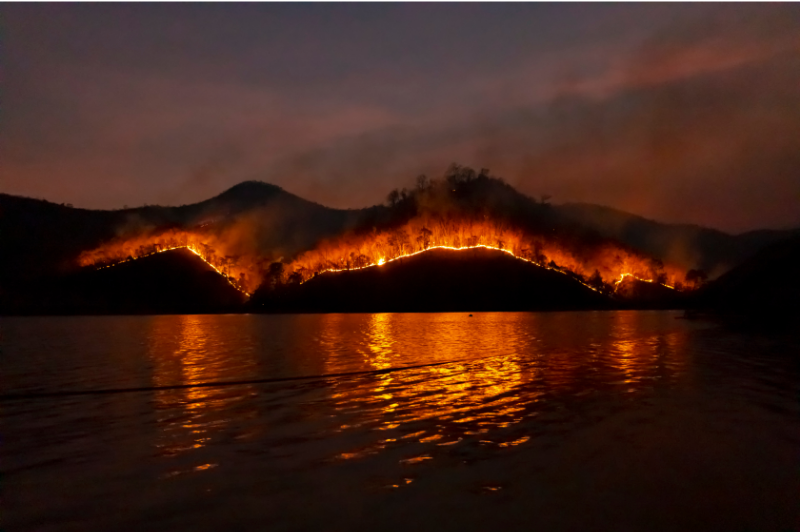
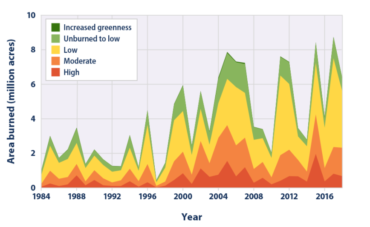
-Wildfires: First responders with access to reliable water transportation systems can stop the spread of wildfire and save lives. Clear, water management systems can also identify areas that are at risk for wildfires and develop fire prevention strategies.
How Can I Get Involved?
If you are interested in helping your community prepare for natural disasters, there are a number of things you can do. Here are a few suggestions:
-Contact your local government and ask how you can get involved in water management planning.
-Attend community meetings and workshops to learn more about water management and how you can help.
-Volunteer with local organizations that work to improve water management in your community.
-Donate to organizations that are working to improve water management in Texas.
Natural disasters can have a devastating impact on communities, but with good water management in place, these communities can be better prepared for the future. If you are interested in helping your community prepare for natural disasters, you can check out our above-ground water transportation solutions.

























 Sales Office Location
Sales Office Location
 sales@portablepipelinesystem.com
sales@portablepipelinesystem.com