
Why California Is Drying Up
California is in the midst of a drought. As populations continue to grow, it’s getting harder for California to maintain its water supplies. Droughts are no strangers to many areas across the world, but they can be mitigated with proper planning and management techniques. In this blog post, we will discuss how droughts happen in California and what can be done about them!
How Long Has California Been In A Drought?
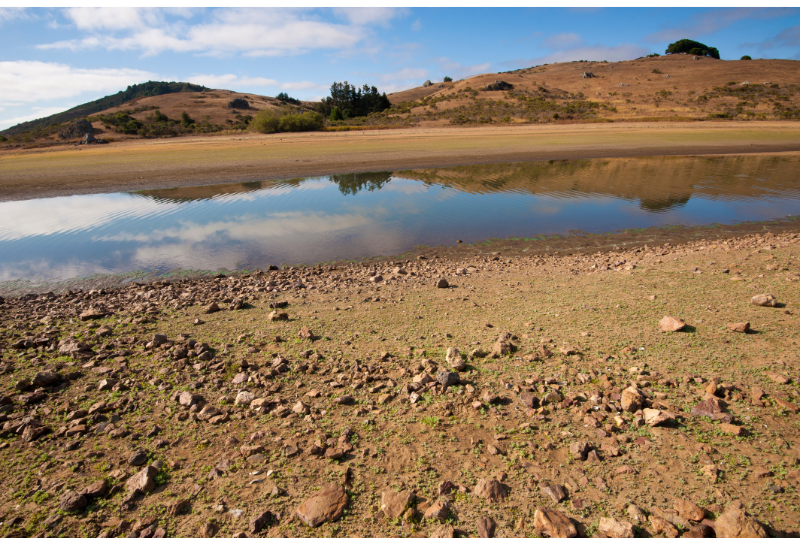
California entered yet another drought in 2021, meaning that at least two consecutive years have been dry, and reservoirs and groundwater stores are depleted.
Since the beginning of the 21st century California has only actually had 3 years that were not considered “dry,” in 2005, 2010, and 2019. Every other year this century can be considered below average in precipitation. However, not all of these years are considered droughts if they are broken by a wet year.
But the difference could be a moot point as the LA times revealed some researchers who believe California has been in the same drought for 20 years, in what is called a Mega-Drought. They suggest that human-caused climate change is behind this issue, making it more difficult to solve.
Of course, not all researchers agree that California has entered a Mega-Drought, but it can’t be argued that conditions are bad. Wet years have become more sporadic, and the state is being forced to reckon with how it utilizes its water resources.
What Are The Effects Of A Drought?
As a drought depletes natural resources, it will eventually adversely affect the people living in that area. One of the hardest-hit areas is agriculture because of the deteriorating groundwater.
Many rural farms rely on nearby groundwater stores as their primary water source. If these dry up, they have nothing to keep their crops alive and provide water for themselves.
Almond crop yields specifically are projected to drop by 10%. There are also generally lower yields across the board and smaller than average citrus fruit.
Across California, small rural communities are poorly prepared for droughts, especially those that rely on shallow wells. We have seen a similar issue in Texas, as major developments have tapped into underground water stores that locals have relied on for years, forcing regular people to drill deeper into the ground for their water.
Conversely, urban areas can utilize water reuse, recycling, and stormwater capture to offset the effects of a flood. It is also no surprise that urban areas use up a majority of the state’s civil water resources.
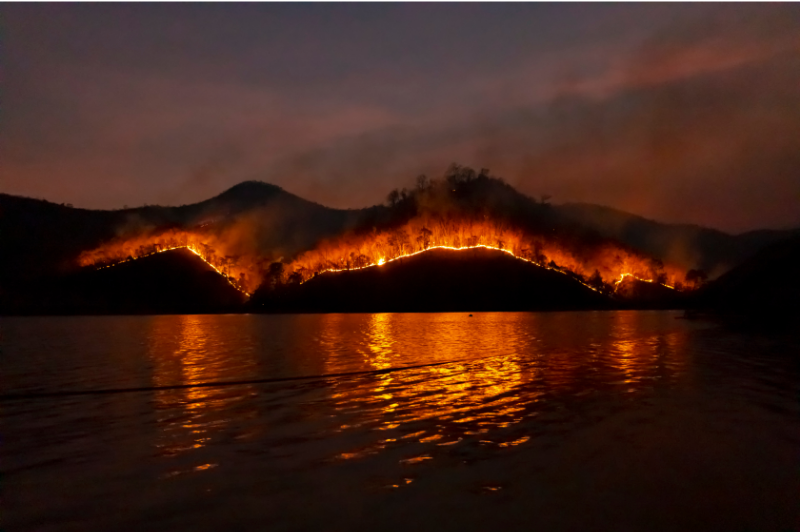
Droughts And Wildfires
One of the most damaging effects of rising temperatures and droughts that we have seen is an increase in the severity of U.S wildfires.
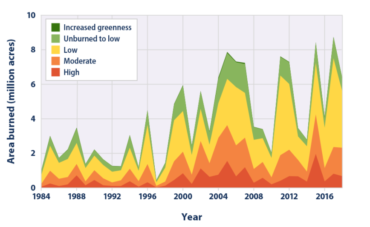
When Will The Drought End?
There is no way to know for sure when the California drought will end, although there have been predictions of the 2022 wet season breaking the streak. For that to happen, there would have to be above average snowfall in the coming winter.
It is important to note that it will take time for the water resources to refill even with a good wet season. It could take upwards of 3-10 years for underground water stores to fill up to reasonable levels after the series of droughts that we have witnessed.
What Can Be Done About The Drought?
The state of California is already in a state of a water emergency, which limits how much water each household can use, but it doesn’t seem to be enough. The longer that the drought goes on, the harder it becomes to manage.
The State Water Project controls the reservoirs, canals, pipelines, and hydroelectric power facilities, but they can’t fix the weather. While expert water management is hugely important to minimizing the draught’s impact, the state will need to maintain its emergency rationing.
State regulators recently announced what could be the state’s first major water storage project in years, which would come in the form of a man-made lake. The new lake would hold enough water to supply 3 million households for a year. However, it is still too early to say if the plan is feasible.
The project would make a massive difference as California’s 1,500 reservoirs are at a historic low and are a critical source of drinking water for the state’s residents.
Wrap Up
There isn’t much that state regulators and officials can do but try to mitigate the effects of California’s drought and hope for a good wet season to come around. In this time when water is more scarce than ever, be sure that your water transportation tools are reliable. Portable Pipeline Systems distributes a number of reliable and flexible potable water-approved flat hoses.






 Sales Office Location
Sales Office Location
 sales@portablepipelinesystem.com
sales@portablepipelinesystem.com